
Futurology could be defined as a science that deals with the study of current trends, which are shaping the conditions for the future development. As a somewhat new branch of science, futurology is an ungrateful business. There are no exact mathematical formulas that enable predictions of the future of the country and humanity, but based on trends, some predictions could be made in that direction.
Where can we see a glimpse of what the future holds
Writers of science fiction have done a great job in the fictional genre. Through many books they have described the possible near and distant future of the world, and many of them are correct, or approximately correct about it. What binds them all together (at least writers from the first half of the 20th century) is optimism in technology progress that is huge, but still it is not so fast. There are also movies and TV shows that represent alternative reality which are also very interesting. For example, a TV show based on the assumptions that Germany won the World War II, The Man in the High Castle. There are many ways in which futurology or futurism tries to predict various aspects of the future, from ambient to political, but we will try to stick to the technological assumption of the future, and the accuracy of predictions of the present from the past.
Assumptions for the future of technology
The assumptions for 22nd century are mostly based on the relationship between humans and robots, or on the development of artificial intelligence and its impact on humans.
Those assumptions go from the apocalyptic, where artificial intelligence destroys humanity, to the symbiosis of man and the computer where consciousness (soul), after bodily death, is uploaded to the cloud and continues its existence there. There are also some predictions of the degradation of technology due to various external influences (meteorite impacts, climate catastrophes etc.) where human species degrades and goes back to times without technology. Moore's Law is a law (perception) that is quite abbreviated and vague, and determines our technological future. According to Wikipedia it is defined as follows: "Moore's law is the observation that the number of transistors in a dense integrated circuit (IC) doubles about every two years." But how does the speed of work actually affect us today? Autonomous cars, i.e. vehicles that drive themselves are based on the speed of the computer. The computer receives information from a large number of sensors, and, in doing so, it makes a decision on how to drive a vehicle in a split second. Those are the decisions that can save a passenger's and other participant's life. All of that would not have been possible with the computing power 15 years ago. Process automation of production, robotics, medical research, transportation, it all depends and develops with the development of speed of work of the computers. One of the important aspects of development is the speed of Internet access, which is also increasing, and new technologies that are coming, especially in wireless connectivity. Those are all influencing future development of new technologies. According to some forecasts, by 2070, we would no longer drive cars, but also cargo ships (which would be completely unmanned), planes or drones. Also, the development of battery capacity allows the predictions of gradual elimination of fossil fuels as we call them, and the transition to renewable forms of energy.
Assumptions for the future of human life
Prolongation of human life is a statistical trend, which brings us some misleading statistics. We don't live much longer than our ancestors, but much more of us survive to those years than a hundred years ago. The average life expectancy is calculated like this - if you have two children, and one dies in childbirth and the other at 75 years, the average life expectancy of your children is 35. Before the development of today's medicine, we had poor child survival statistics. If between 1200 and 1745, you lived until your 21st birthday, you had a high probability of surviving to the age of 65, which is not much shorter than today, but you were very lucky if you survived until that 21st birthday.
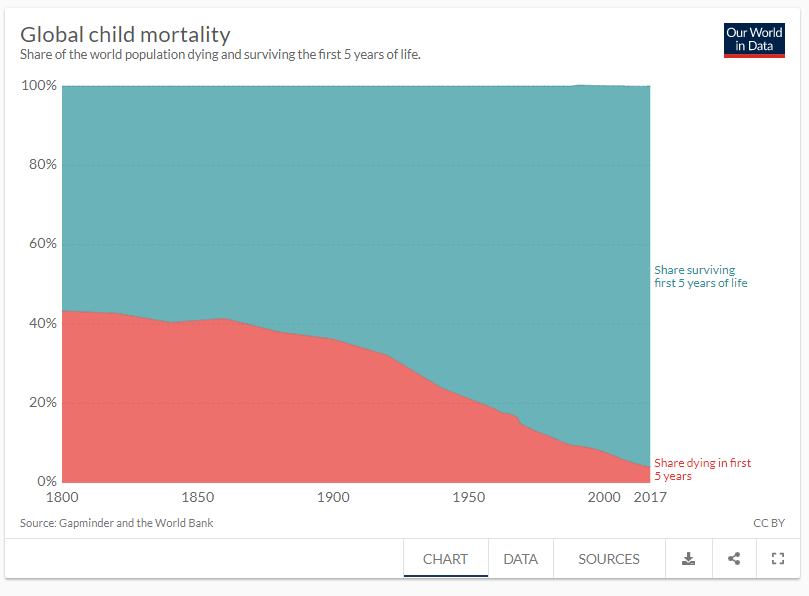
Here we come to a new problem for the future of the human race - overcrowding. There are now 7.3 billion people on Earth, and the UN is assuming there will be about 9.7 billion people in 2050, and 11 billion in 2100. There is no similar example of population growth in the past of the human race so the predictions cannot be based on experiences. The problem is not seen in the number of people, but in the number of consumers of energy and natural resources. That problem was once solved by emigration to the colonies, the places which had far more resources. In this way, SciFi writers also assumed that the problem of overcrowding could be solved by the expansion of the human race into space, but we have not made much progress yet. After going to the Moon, man did not go further into space. Technology has advanced, but the big problem is the adaptation of the human body to life in space, from the problem of radiation, to harsh conditions on planets or satellites such as Mars and the Moon. Until the appearance of Elon Musk, the outcome of going into space was not likely, but with his ideas and the ways to reduce prices of space flights opened the way for humans to stay on the Moon, and later on Mars.

When we talk about the future there is not a single assumption. Every decision we make in life is taking us into one of our alternative futures. All the same, humanity's decisions globally create a better or worse future for the mankind. For now, we know that the future of everyday life is strongly tied to technology, but through education we should especially work to return the people to nature, and to create a positive synergy of technology, people and nature to leave our children the world where life is possible and good.

